This is a mirror page, please see the original page:
https://xmake.io/#/plugin/more_pluginsVSCode Plugin
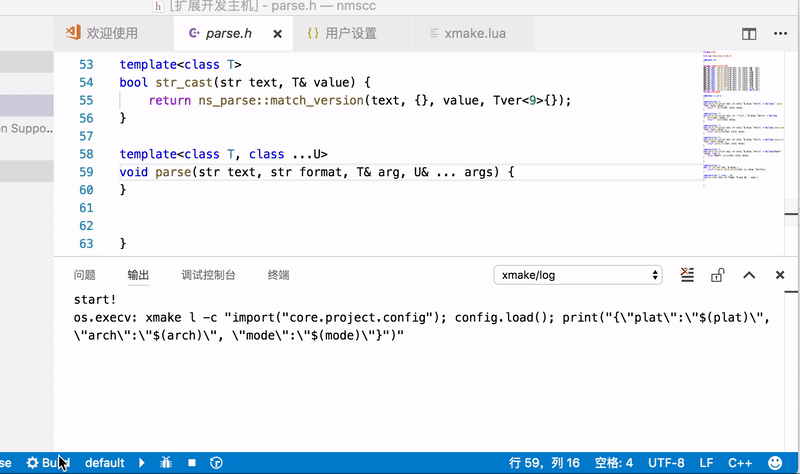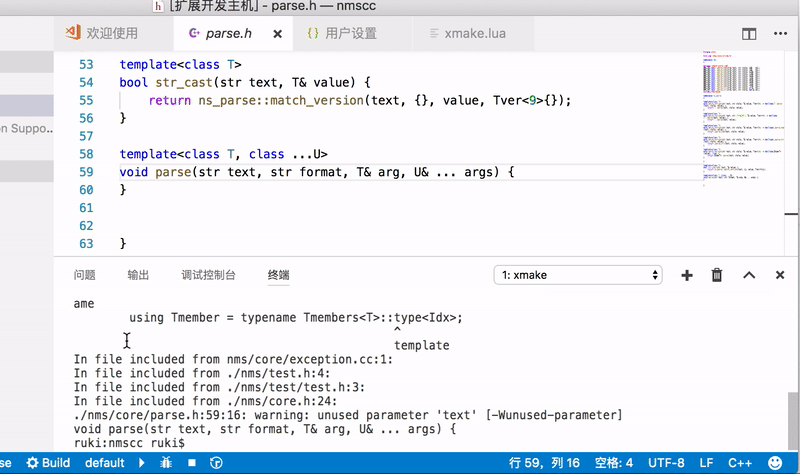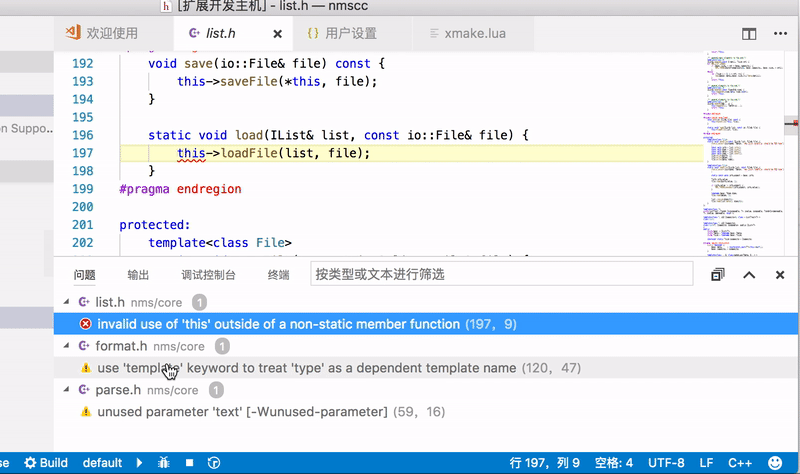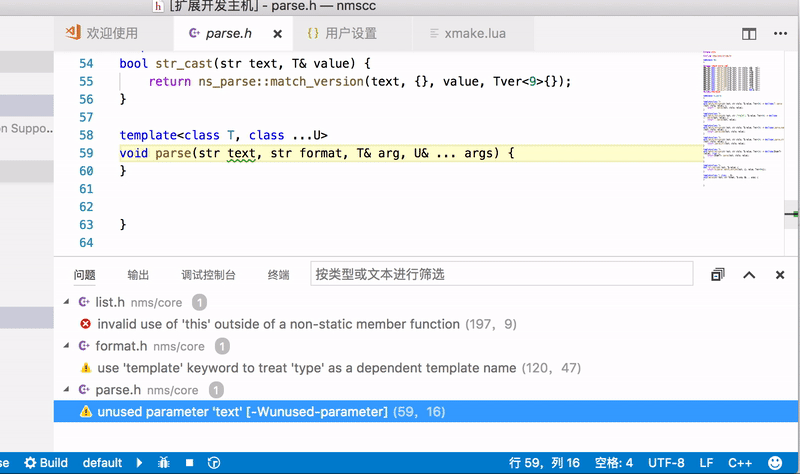
VSCodeis a commonly used text editor, and xmake provides plug-ins' support.
Plugin installation
Since VSCode itself only provides text editing functions, we need to install plug-ins to support configuration, compilation, debugging, intellisenses and other functions:
- XMake
- C/C++
- CodeLLDB
After completing the installation of the plug-in, restart VSCode to see the status bar below:
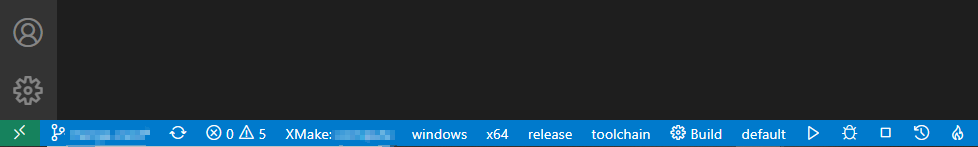
You can set the platform, architecture, compilation mode, tool-chain and other options in the status bar, and then click Build to start the build.
Custom options
If these options are not enough, you can create .vscode/settings.json and write the settings required by xmake, such as:
{
...
"xmake.additionalConfigArguments": [
"--my_option=true"
],
...
}
Other xmake options can also be setted in settings.json. After modification, the configuration can be refreshed through the >XMake: Configure command.
Configure Intellsence
For a better C++ syntax prompt experience, xmake provides support for Language Server Protocol (LSP for short).
In vscode, we can provide intellsence support by using vscode-cpptools or clangd.
In addition, in order to support intellsence, xmake provides compile_commands.json generation support.
generate compile_commands
Automatic trigger generation
Usually after modifying xmake.lua and clicking Save, the xmake-vscode plugin will trigger the automatic generation of compile_commands.json, which is stored in the .vscode directory by default.
This is also the recommended way. Usually after installing the xmake-vscode plug-in and opening the project with xmake.lua, you only need to edit xmake.lua to save and trigger without any other additional operations.
Manually trigger generation
Of course, if we don’t see the file being generated, we can also use the >XMake: UpdateIntellisense command to manually trigger the generation of .vscode/compile_commands.json in vscode.
Configure xmake.lua to generate automatically
Alternatively, we can also use this rule to automatically update and generate compile_commandss.json
add_rules("plugin.compile_commands.autoupdate", {outputdir = ".vscode"})
target("test")
set_kind("binary")
add_files("src/*.c")
This will automatically update this file after each build.
Manual execution command generation
If the above methods are invalid, we can also execute the command to generate.
$ xmake project -k compile_commands .vscode
vscode-cpptools
If we use the vscode-cpptools plug-in to provide intellsence support, we need to go to the vscode plug-in market first, search for C++, the default first plug-in is to install it.
When installed, this plugin provides intellsence and debugging support.
Then, we need to configure the c_cpp_properties.json file and associate it with the .vscode/compile_commands.json we generated.
{
"env": {
"myDefaultIncludePath": ["${workspaceFolder}", "${workspaceFolder}/include"],
"myCompilerPath": "/usr/local/bin/gcc-7"
},
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Mac",
"intelliSenseMode": "clang-x64",
"includePath": ["${myDefaultIncludePath}", "/another/path"],
"macFrameworkPath": ["/System/Library/Frameworks"],
"defines": ["FOO", "BAR=100"],
"forcedInclude": ["${workspaceFolder}/include/config.h"],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"compileCommands": "/path/to/compile_commands.json",
"browse": {
"path": ["${workspaceFolder}"],
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": ""
}
}
],
"version": 4
}
That is the "compileCommands": "/path/to/compile_commands.json" configuration item above.
For how to open this configuration file, and more configuration instructions, see:
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/configure-intellisense-crosscompilation
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/c-cpp-properties-schema-reference
Of course, in theory, the xmake-vscode plugin can automatically associate and set this file, but considering that users do not necessarily use cpptools, they may also use clangd.
Therefore, the default automatic configuration is not very good, and the author has no time and energy to improve it.
clangd
When using clangd, there may be conflicts with the C/C++ plug-in, you can add settings in .vscode/settings.json:
{
"C_Cpp.codeAnalysis.runAutomatically": false,
"C_Cpp.intelliSenseEngine": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.formatting": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.autoAddFileAssociations": false,
"C_Cpp.autocompleteAddParentheses": false,
"C_Cpp.autocomplete": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.errorSquiggles": "Disabled",
...
}
Also, since the compile_commands.json generated by XMake is in the .vscode directory, you need to set the clangd parameter to look for it in the correct location:
{
"clangd.arguments": [
"--compile-commands-dir=.vscode",
...
]
...
}
Sublime Plugin
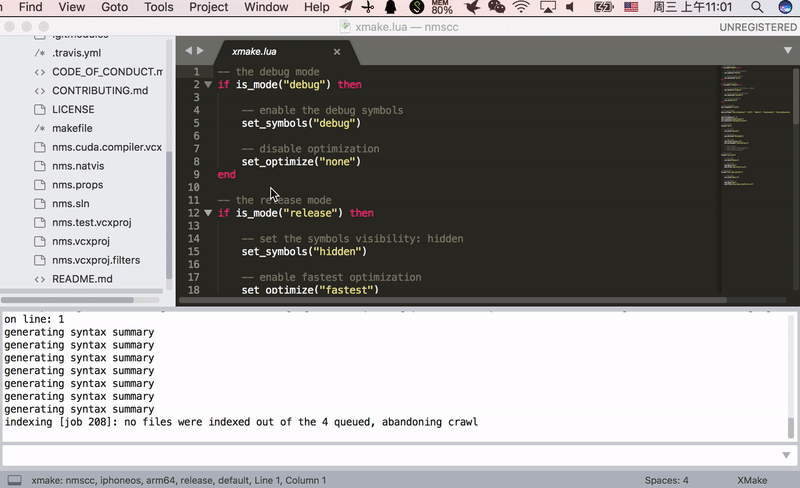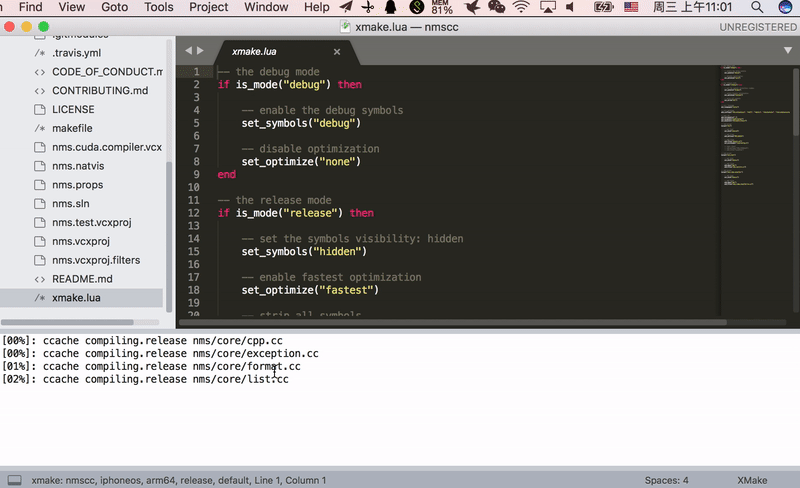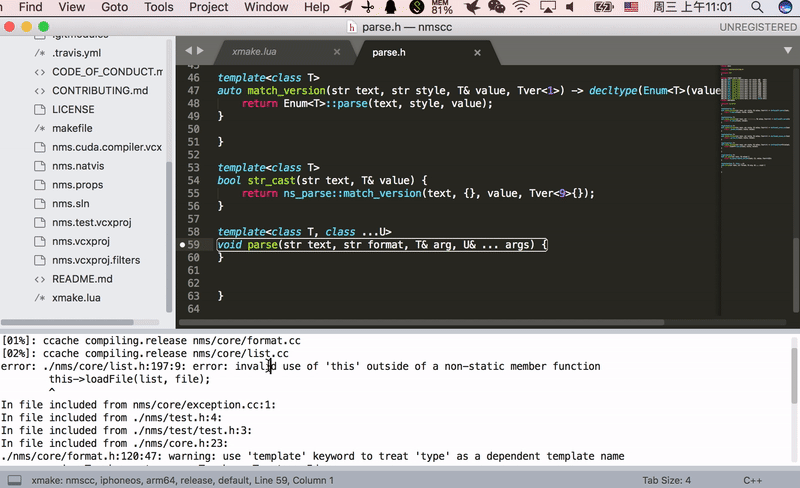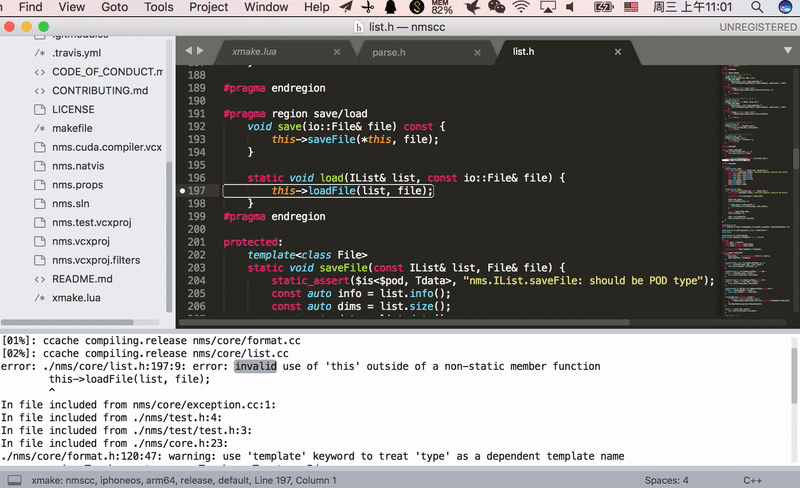
Intellij IDEA/Clion Pluin
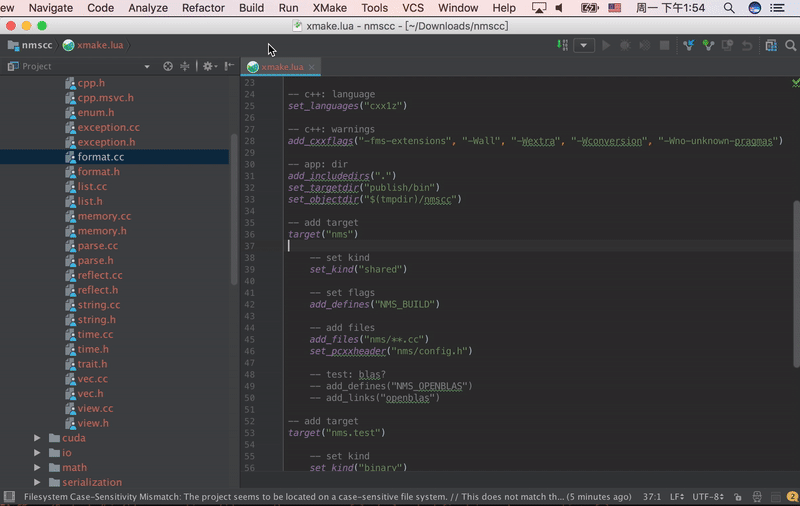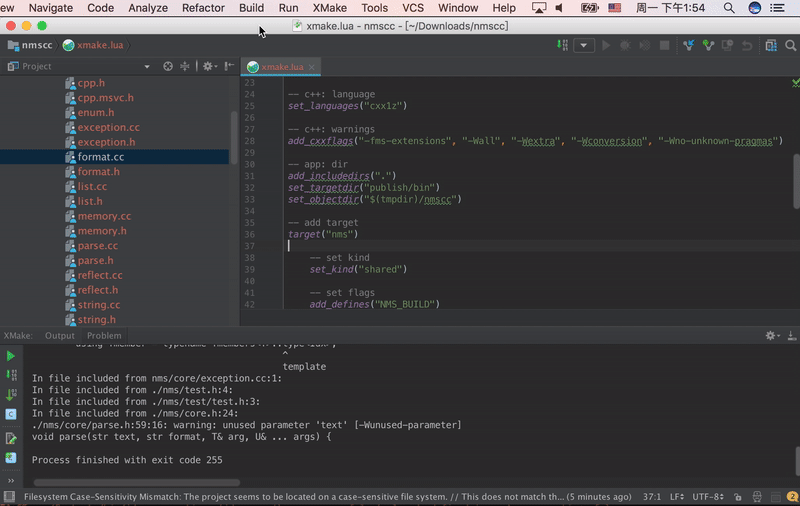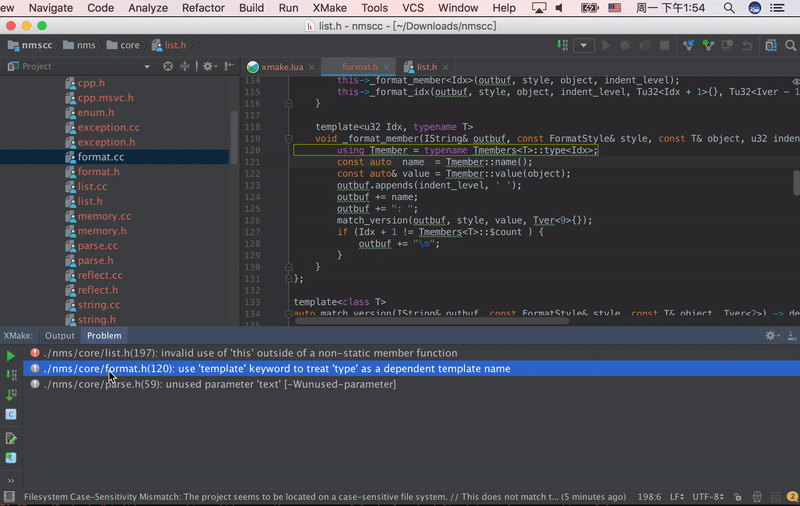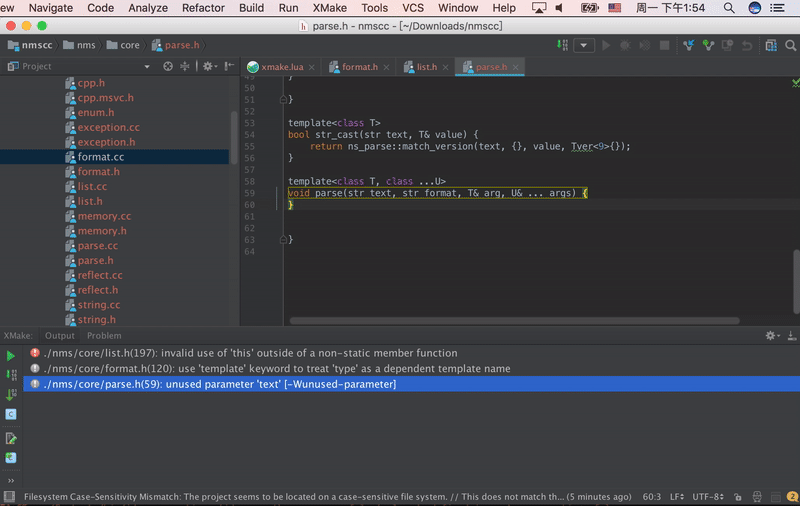
Vim Plugin
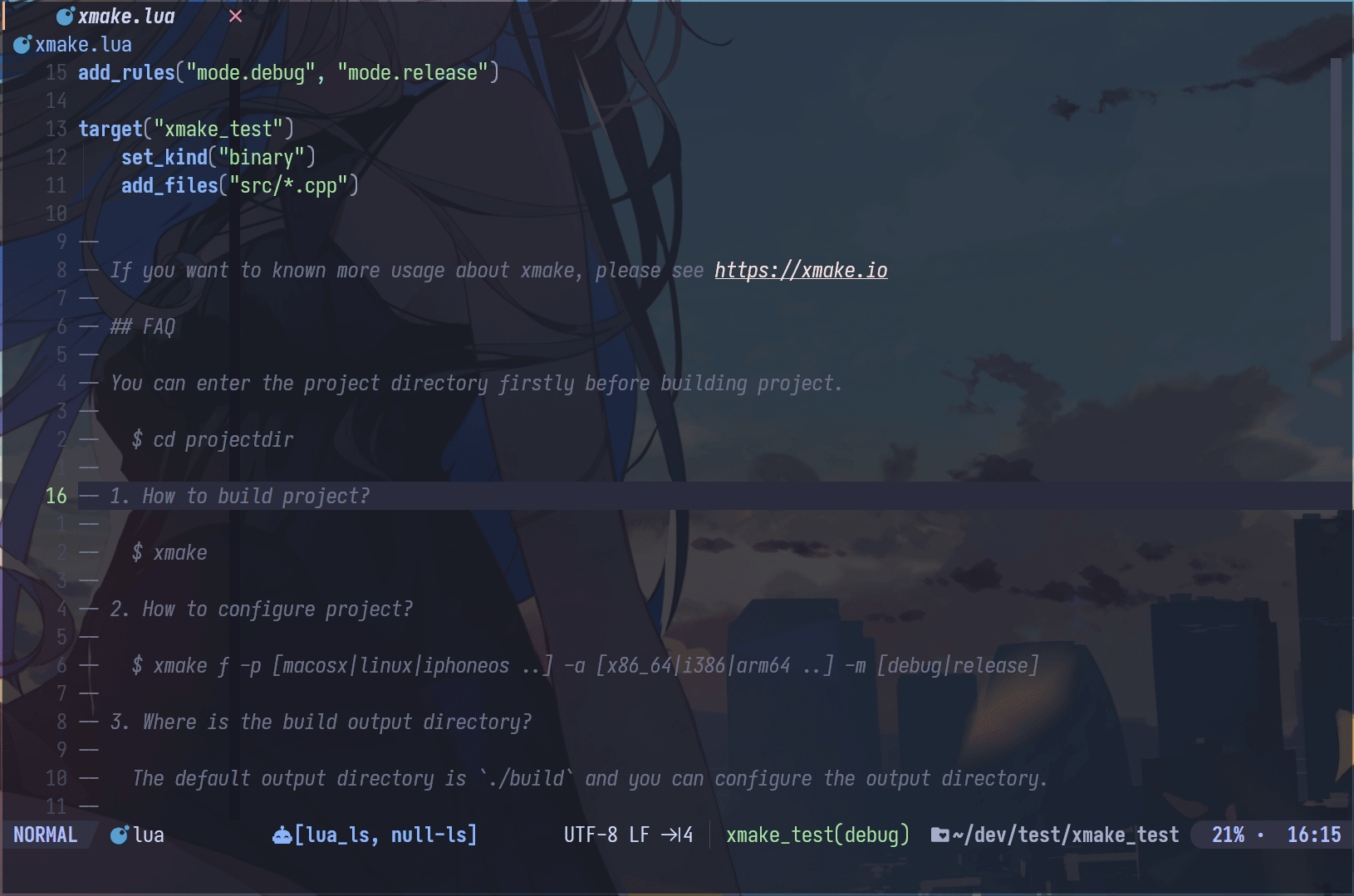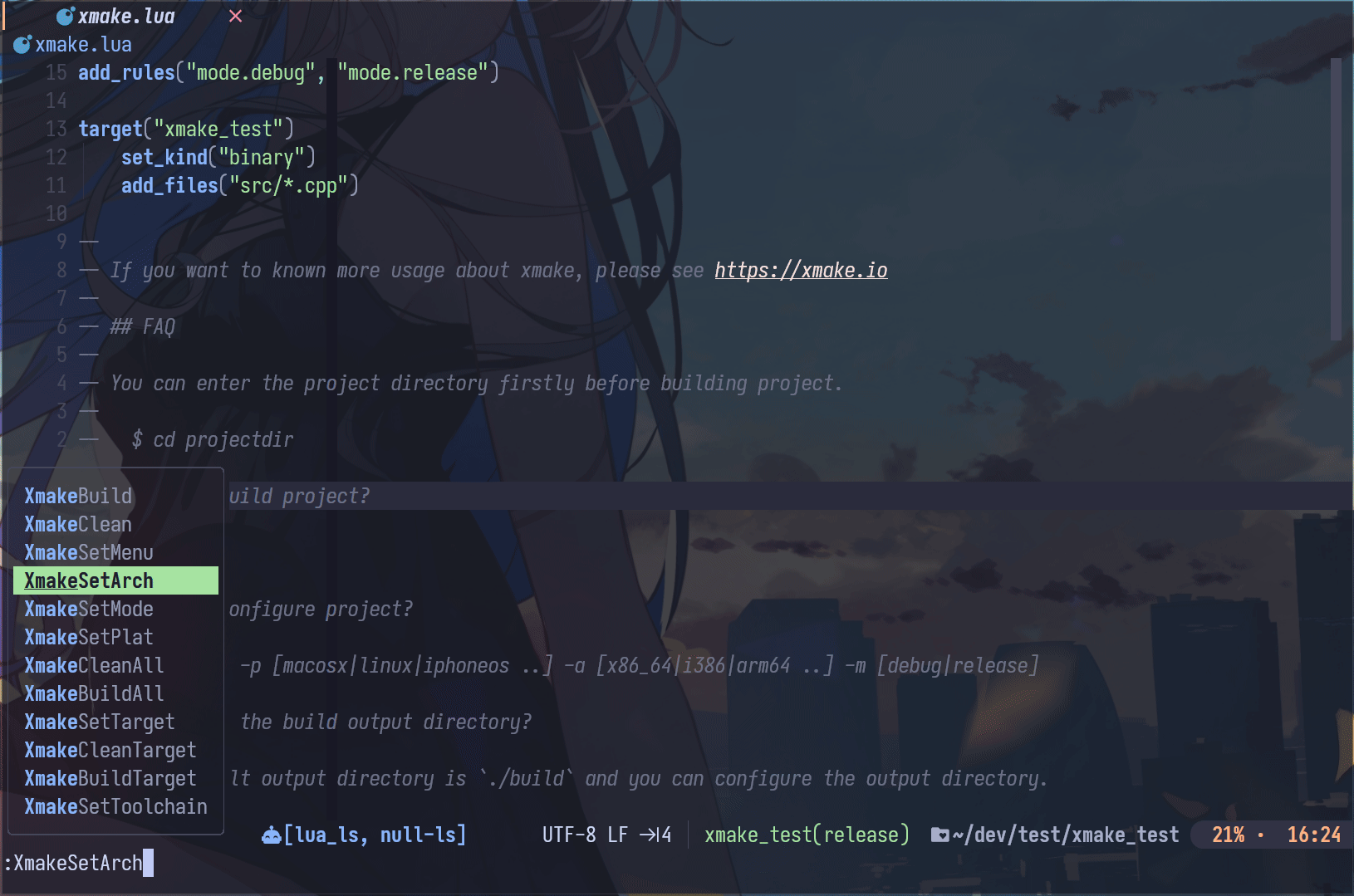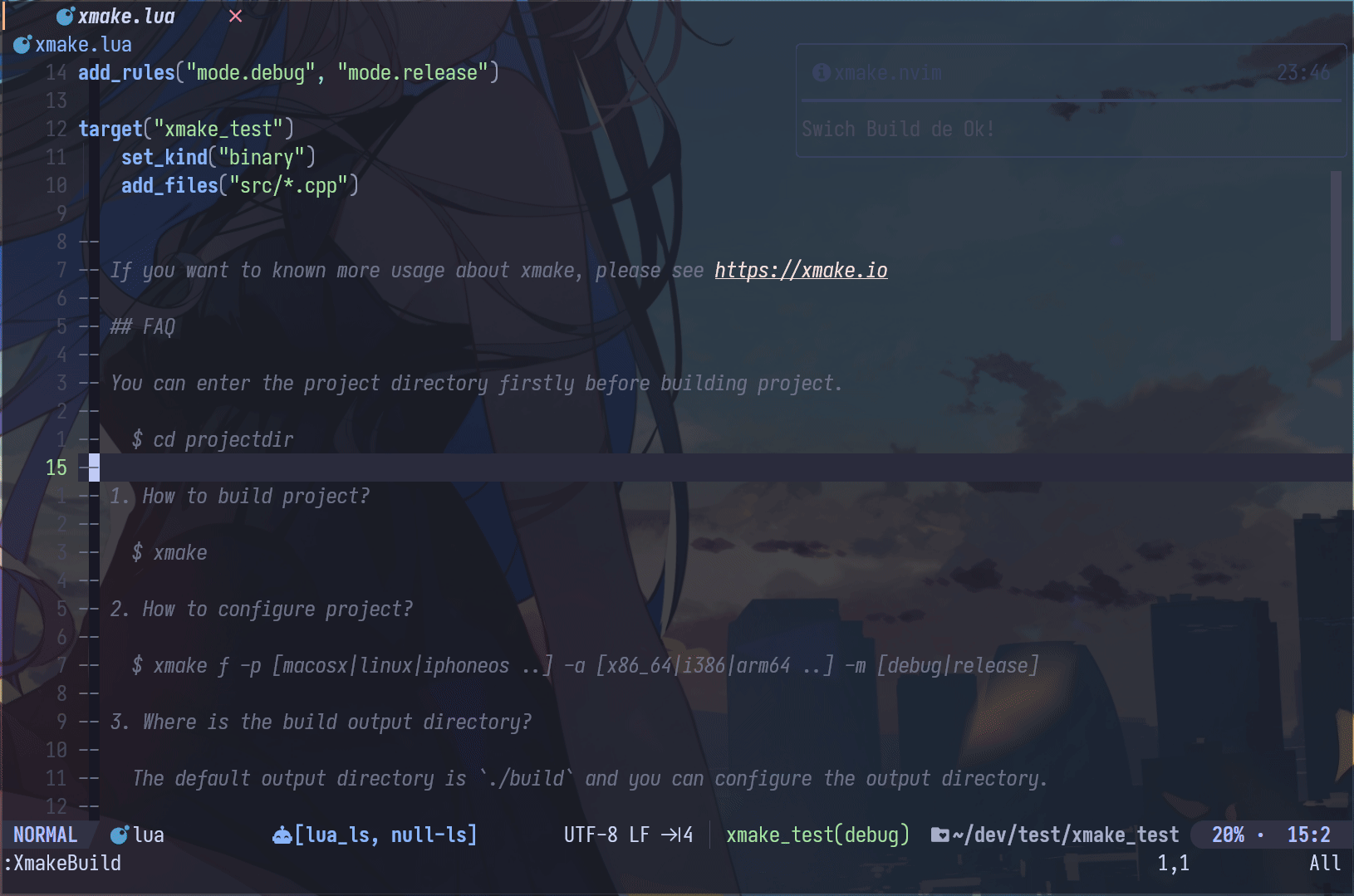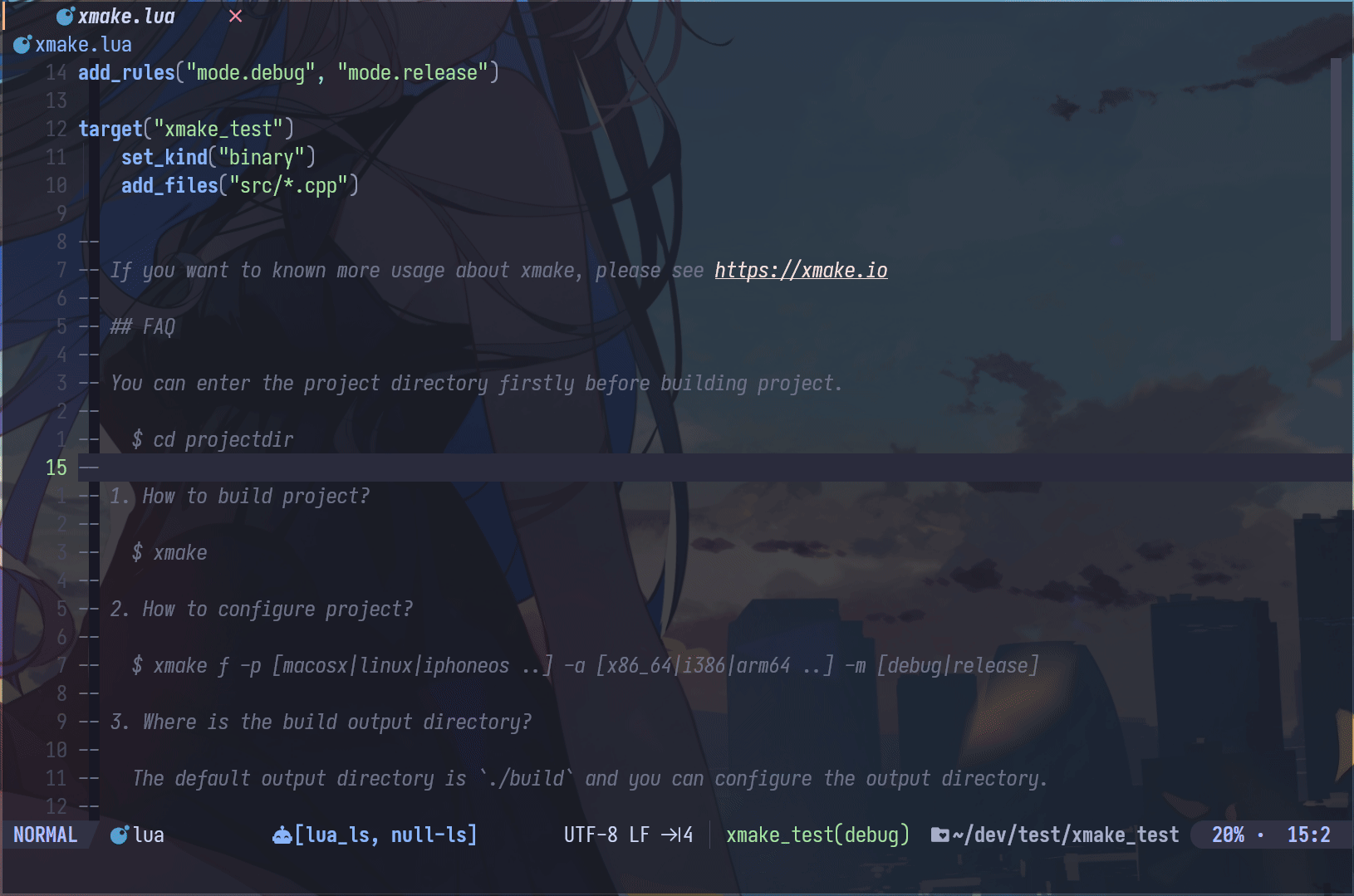
Neovim Plugin
- xmake.nvim (third-party, thanks @Mythos_404)
The plugin provides easy-to-use configuration UI and auto-generation of compile_commands.json files
Gradle Plugin (JNI)
- xmake-gradle: A gradle plugin that integrates xmake seamlessly
plugins DSL
plugins {
id 'org.tboox.gradle-xmake-plugin' version '1.0.9'
}
Legacy plugin application
buildscript {
repositories {
maven {
url "https://plugins.gradle.org/m2/"
}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.tboox:gradle-xmake-plugin:1.0.9'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
}
apply plugin: "org.tboox.gradle-xmake-plugin"
Simplest Example
We add xmake.lua to projectdir/jni/xmake.lua and enable xmake in build.gradle.
build.gradle
android {
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
path "jni/xmake.lua"
}
}
}
JNI
The JNI project structure:
projectdir
- src
- main
- java
- jni
- xmake.lua
- *.cpp
xmake.lua:
add_rules("mode.debug", "mode.release")
target("nativelib")
set_kind("shared")
add_files("nativelib.cc")
More Gradle Configuations
android {
defaultConfig {
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
// append the global cflags (optional)
cFlags "-DTEST"
// append the global cppflags (optional)
cppFlags "-DTEST", "-DTEST2"
// switch the build mode to `debug` for `xmake f -m debug` (optional)
buildMode "debug"
// set abi filters (optional), e.g. armeabi, armeabi-v7a, arm64-v8a, x86, x86_64
// we can also get abiFilters from defaultConfig.ndk.abiFilters
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a"
}
}
}
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
// enable xmake and set xmake.lua project file path
path "jni/xmake.lua"
// enable verbose output (optional), e.g. verbose, warning, normal
logLevel "verbose"
// set c++stl (optional), e.g. c++_static/c++_shared, gnustl_static/gnustl_shared, stlport_static/stlport_shared
stl "c++_shared"
// set the given xmake program path (optional)
// program /usr/local/bin/xmake
// disable stdc++ library (optional)
// stdcxx false
// set the given ndk directory path (optional)
// ndk "/Users/ruki/files/android-ndk-r20b/"
// set sdk version of ndk (optional)
// sdkver 21
}
}
}
Build JNI and generate apk
The xmakeBuild will be injected to assemble task automatically if the gradle-xmake-plugin has been applied.
$ ./gradlew app:assembleDebug
> Task :nativelib:xmakeConfigureForArm64
> Task :nativelib:xmakeBuildForArm64
>> xmake build
[ 50%]: cache compiling.debug nativelib.cc
[ 75%]: linking.debug libnativelib.so
[100%]: build ok!
>> install artifacts to /Users/ruki/projects/personal/xmake-gradle/nativelib/libs/arm64-v8a
> Task :nativelib:xmakeConfigureForArmv7
> Task :nativelib:xmakeBuildForArmv7
>> xmake build
[ 50%]: cache compiling.debug nativelib.cc
[ 75%]: linking.debug libnativelib.so
[100%]: build ok!
>> install artifacts to /Users/ruki/projects/personal/xmake-gradle/nativelib/libs/armeabi-v7a
> Task :nativelib:preBuild
> Task :nativelib:assemble
> Task :app:assembleDebug
Force to rebuild JNI
$ ./gradlew nativelib:xmakeRebuild