This is a mirror page, please see the original page:
https://xmake.io/#/manual/configuration_optionDefine and set option switches. Each option corresponds to an option that can be used to customize the build configuration options and switch settings.
!> All domain interfaces except target, such as option, task, etc., cannot be placed in the outer global scope by default (unless some interfaces are shared with the target).
If you want to set the value to affect all options such as option, task, you can set it by anonymous global domain.
E.g:
-- Enter the anonymous global domain of the option, the settings inside will affect the test and test2 options.
option()
add_defines("DEBUG")
option("test")
-- ...
-- Try to keep indented, because all settings after this are for the test option.
option("test2")
-- ...
!> The option field can be repeatedly entered to implement separate settings. If you want to display the scope settings away from the current option, you can manually call the option_end interface.
option
Defining options
Define and set option switches for custom compilation configuration options, switch settings.
For example, define an option to enable test:
option("test")
set_default(false)
set_showmenu(true)
add_defines("TEST")
Then associate it with the specified target:
target("demo")
add_options("test")
Thus, if an option is defined, if this option is enabled, the macro definition of -DTEST will be automatically added when compiling the target.
# Manually enable this option
$ xmake f --test=y
$ xmake
option_end
End definition option
This is an optional api that shows the departure option scope, similar to target_end.
option:add_deps
Adding options depends
By setting the dependency, you can adjust the detection order of the options, which is generally used when the detection script is called by on_check.
option("small")
set_default(true)
on_check(function (option)
-- ...
end)
option("test")
add_deps("small")
set_default(true)
after_check(function (option)
if option:dep("small"):enabled() then
option:enable(false)
end
end)
After the detection of the dependent small option is completed, the state of the option of the test is controlled by judging the state of the small option.
!> Since on_check will only be executed when the default value is not set, if the default value is set, the custom logic can be processed in the after_check phase.
option:before_check
Execute this script before option detection
option("zlib")
before_check(function (option)
end)
option:on_check
Custom Option Detection Script
This script overrides the built-in option detection logic.
option("test")
add_deps("small")
on_check(function (option)
if option:dep("small"):enabled() then
option:enable(false)
end
end)
If the option that test depends on passes, disable the test option.
!> Only when set_default is not set, will the on_check be executed for custom option check script.
option:after_check
Execute this script after option detection
After the option detection is complete, execute this script for some post-processing, or you can re-disable the option at this time:
option("test")
add_deps("small")
add_links("pthread")
after_check(function (option)
option:enable(false)
end)
option:set_values
Setting the list of option values
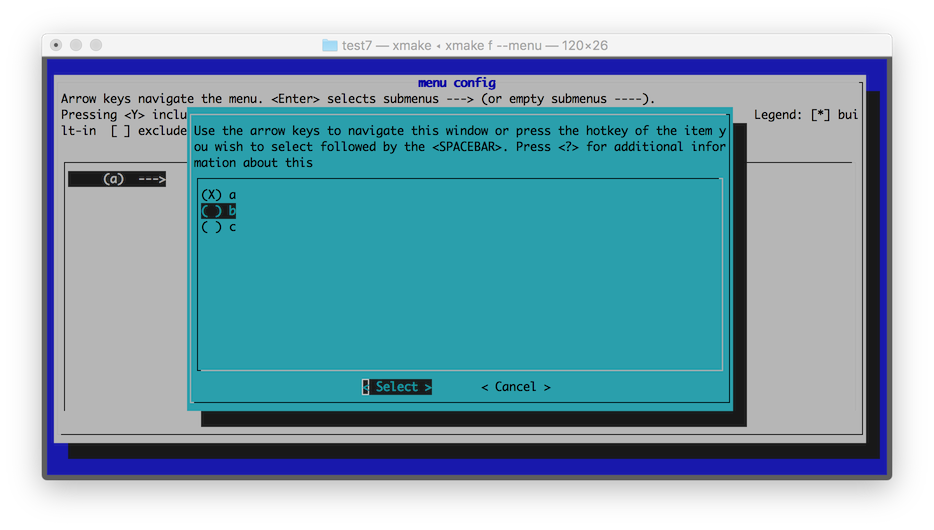
For the graphical menu configuration of xmake f --menu only, a list of option values is provided for quick selection by the user, for example:
option("test")
set_default("b")
set_showmenu(true)
set_values("a", "b", "c")
The effect chart is as follows:
option:set_default
Setting options defaults
When the option value is not modified by the command xmake f --option=[y|n}, the option itself has a default value, which can be set through this interface:
option("test")
-- This option is disabled by default
set_default(false)
The value of the option supports not only the boolean type but also the string type, for example:
option("test")
set_default("value")
| Value Type | Description | Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | Typically used as a parameter switch, value range: true/false |
xmake f --optionname=[y/n/yes/no/true/false] |
| string | can be any string, generally used for pattern judgment | xmake f --optionname=value |
If it is an option of the boolean value, it can be judged by has_config, and the option is enabled.
If it is an option of type string, it can be used directly in built-in variables, for example:
-- define a path configuration option, using the temporary directory by default
option("rootdir")
set_default("$(tmpdir)")
set_showmenu(true)
target("test")
-- add source files in the specified options directory
add_files("$(rootdir)/*.c")
Among them, $(rootdir) is a custom option built-in variable, which can be dynamically modified by manual configuration:
$ xmake f --rootdir=~/projectdir/src
$ xmake
Specify a different source directory path for this rootdir option and compile it.
Detection behavior of the option:
| default value | detection behavior |
|---|---|
| No setting | Priority manual configuration modification, disabled by default, otherwise automatic detection, can automatically switch boolean and string type according to the type of value manually passed in |
| false | switch option, not automatic detection, disabled by default, can be manually configured to modify |
| true | switch option, not automatic detection, enabled by default, can be manually configured to modify |
| string type | no switch state, no automatic detection, can be manually configured and modified, generally used for configuration variable transfer |
option:set_showmenu
Set whether to enable menu display
If set to true, then this option will appear in xmake f --help, which can also be configured via xmake f --optionname=xxx, otherwise it can only be used inside xmake.lua , the modification cannot be configured manually.
option("test")
set_showmenu(true)
After setting the menu to enable, execute xmake f --help to see that there is one more item in the help menu:
Options:
...
--test=TEST
!> After 2.6.8, this option is enabled by default and there is usually no need to configure it additionally.
option:set_category
Setting option categories, only for menu display
This is an optional configuration, only used in the help menu, the classification display options, the same category of options, will be displayed in the same group, so the menu looks more beautiful.
E.g:
option("test1")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("test")
option("test2")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("test")
option("demo1")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("demo")
option("demo2")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("demo")
The four options here are grouped into two groups: test and demo, and the layout shown is similar to this:
Options:
...
--test1=TEST1
--test2=TEST2
--demo1=DEMO1
--demo2=DEMO2
This interface is just to adjust the display layout, more beautiful, no other use.
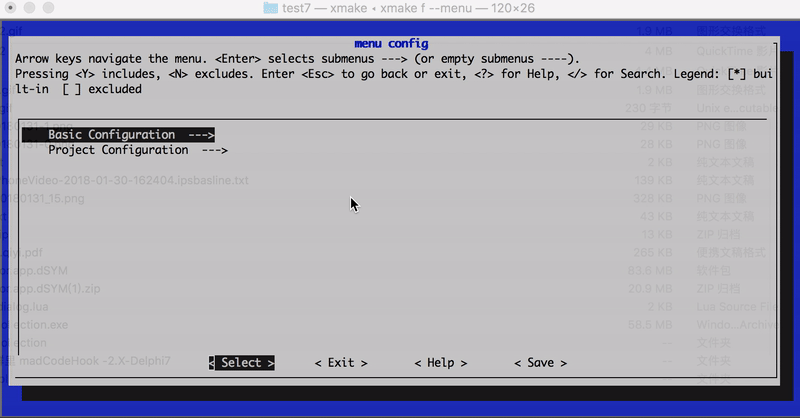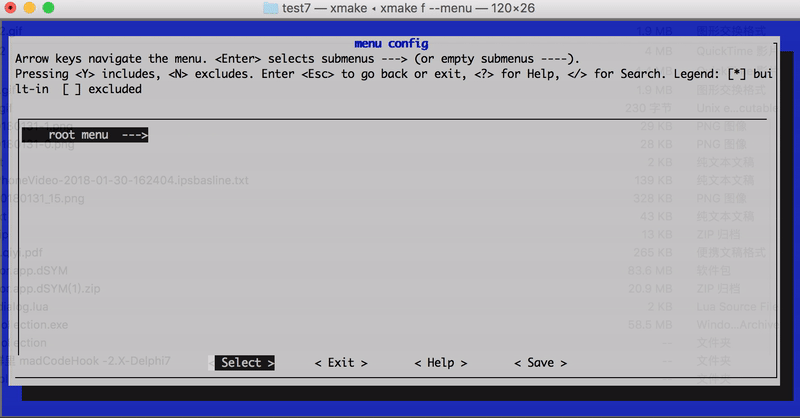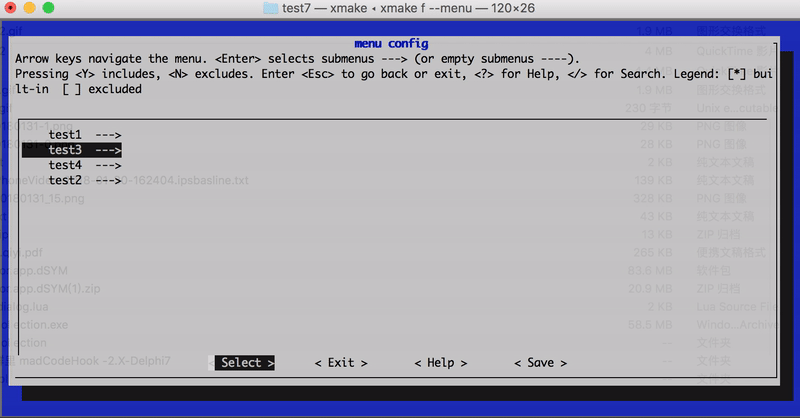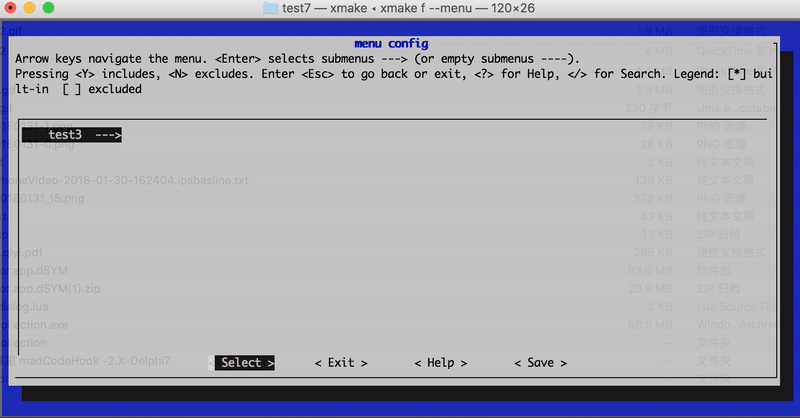
In version 2.1.9, the hierarchical path name set_category("root/submenu/submenu2") can be set via category to configure the graphical menu interface of xmake f --menu, for example:
-- 'boolean' option
option("test1")
set_default(true)
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("root menu/test1")
-- 'choice' option with values: "a", "b", "c"
option("test2")
set_default("a")
set_values("a", "b", "c")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("root menu/test2")
-- 'string' option
option("test3")
set_default("xx")
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("root menu/test3/test3")
-- 'number' option
option("test4")
set_default(6)
set_showmenu(true)
set_category("root menu/test4")
The menu interface path structure finally displayed in the above configuration:
- root menu
- test1
- test2
- test3
- test3
- test4
The effect chart is as follows:
option:set_description
Setting menu display description
When the option menu is displayed, the description on the right is used to help the user know more clearly about the purpose of this option, for example:
option("test")
set_default(false)
set_showmenu(true)
set_description("Enable or disable test")
The generated menu contents are as follows:
Options:
...
--test=TEST Enable or disable test (default: false)
This interface also supports multi-line display and outputs more detailed description information, such as:
option("mode")
set_default("debug")
set_showmenu(true)
set_description("Set build mode",
" - debug",
" - release",
"-profile")
The generated menu contents are as follows:
Options:
...
--mode=MODE Set build mode (default: debug)
- debug
- release
- profile
When you see this menu, the user can clearly know the specific use of the defined mode option and how to use it:
$ xmake f --mode=release
option:add_links
Add Link Library Detection
If the specified link library is passed, this option will be enabled and the associated target will automatically be added to this link, for example:
option("pthread")
add_links("pthread")
add_linkdirs("/usr/local/lib")
target("test")
add_options("pthread")
If the test passes, the test target will be automatically added when it is compiled: -L/usr/local/lib -lpthread compile option
option:add_linkdirs
Adding the search directory needed for link library detection
This is optional. Generally, the system library does not need to add this, and it can also pass the test. If it is not found, you can add the search directory yourself to improve the detection pass rate. For details, see: add_links
option:add_rpathdirs
Adding a load search directory for a dynamic library at runtime
After the option passes the detection, it will be automatically added to the corresponding target. For details, see: target.add_rpathdirs.
option:add_cincludes
Add c header file detection
This option will be enabled if the c header file is passed, for example:
option("pthread")
add_cincludes("pthread.h")
add_defines("ENABLE_PTHREAD")
target("test")
add_options("pthread")
This option checks if there is a pthread.h header file. If the test passes, then the test target program will add the macro definition of ENABLE_PTHREAD.
If you want more flexible detection, you can do this in option.on_check via lib.detect.has_cincludes.
option:add_cxxincludes
Add c++ header file detection
Similar to add_cincludes, except that the detected header file type is a c++ header file.
option:add_ctypes
Add c type detection
This option will be enabled if the c type is passed, for example:
option("wchar")
add_ctypes("wchar_t")
add_defines("HAVE_WCHAR")
target("test")
add_options("wchar")
This option checks if there is a type of wchar_t. If the test passes, then the test target program will add the macro definition of HAVE_WCHAR.
If you want more flexible detection, you can do this in option.on_check via lib.detect.has_ctypes.
option:add_cxxtypes
Adding c++ type detection
Similar to add_ctypes, except that the type detected is a c++ type.
option:add_csnippets
Add c code fragment detection
If the existing add_ctypes, add_cfuncs, etc. cannot meet the current detection requirements,
You can use this interface to implement more custom detection of some compiler feature detection, see: add_cxxsnippets.
option:add_cxxsnippets
Adding c++ code snippet detection
This interface can be used to implement more custom detection of some compiler feature detection, especially the detection support of various features of C++, such as:
option("constexpr")
add_cxxsnippets("constexpr", "constexpr int f(int x) { int sum=0; for (int i=0; i<=x; ++i) sum += i; return sum; } constexpr int x = f (5); static_assert(x == 15);")
The first parameter sets the name of the code snippet as a label, and is displayed when the output information is detected.
The above code implements the detection of the constexpr feature of C++. If the test passes, the constexpr option is enabled. Of course, this is just an example.
For the detection of compiler features, there is a more convenient and efficient detection module, providing more powerful detection support, see: compiler.has_features and detect.check_cxsnippets
If you want more flexible detection, you can do this in option.on_check via lib.detect.check_cxsnippets.
After v2.5.7, two new options, {tryrun = true} and {output = true}, are added to try to run detection and capture output.
Setting tryrun can try to run to detect:
option("test")
add_cxxsnippets("HAS_INT_4", "return (sizeof(int) == 4)? 0: -1;", {tryrun = true})
Setting output will also try to detect and additionally capture the output content of the run.
option("test")
add_cxxsnippets("INT_SIZE",'printf("%d", sizeof(int)); return 0;', {output = true, number = true})
!> Set to capture output, the current option cannot set other snippets
We can also get the output bound to the option through is_config.
if is_config("test", "8") then
- xxx
end
option:add_cfuncs
Add c library function detection
option("setjmp")
add_cincludes("setjmp.h")
add_cfuncs("sigsetjmp", "setjmp")
add_defines("HAVE_SETJMP")
target("test")
add_options("setjmp")
This option detects whether there are some interfaces of setjmp. If the test passes, the target program of test will add the macro definition of HAVE_SETJMP.
The function fragments inside support the following syntax formats:
-- Simply detect whether the function address exists, and internally will try to determine its address
sigsetjmp
-- If some functions are defined by macro wrap, the detection can be bypassed in this way
sigsetjmp((void*)0, 0)
-- You can also specify a complete function statement, for example: funcname{codebody}
sigsetjmp{sigsetjmp((void*)0, 0);}
sigsetjmp{int a = 0; sigsetjmp((void*)a, a);}
Note that the detected function usually needs to be accompanied by add_cincludes to ensure that the function can be included normally, otherwise the detection will fail.
option:add_cxxfuncs
Add c++ library function detection
The usage is consistent with option:add_cfuncs.