IDE Integration Plugins
VSCode Plugin
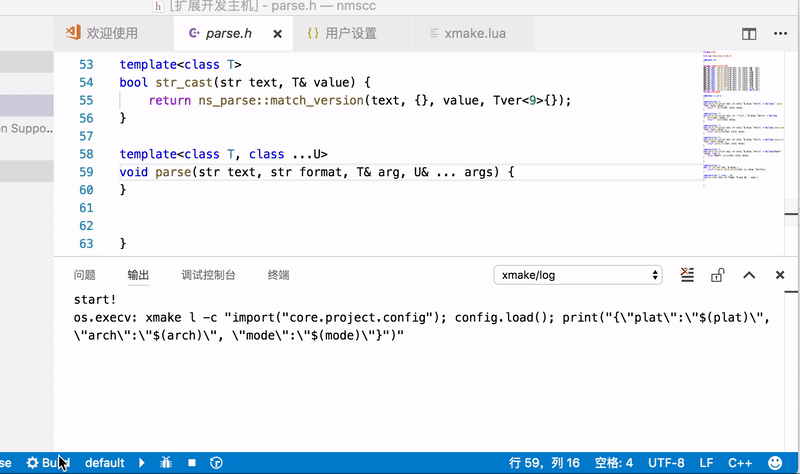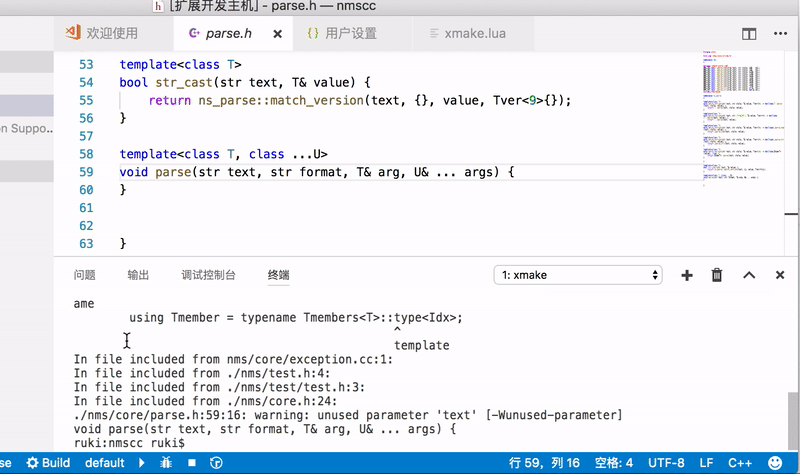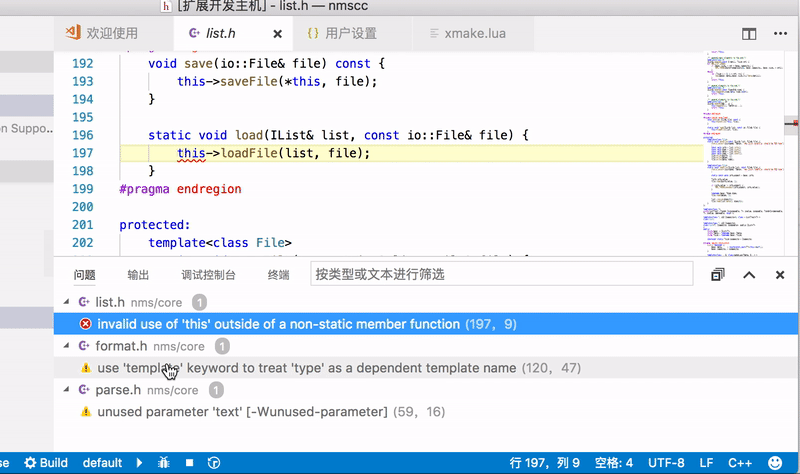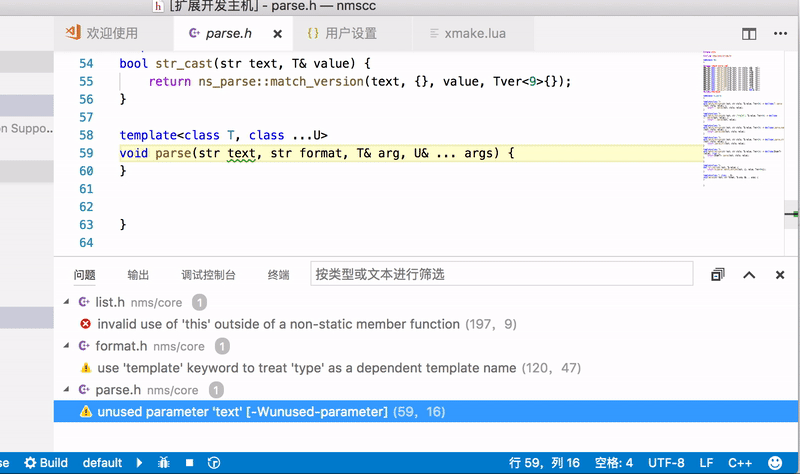
VSCode is a commonly used text editor, and xmake provides plugin support.
Plugin installation
Since VSCode itself only provides text editing functions, we need to install plugins to support configuration, compilation, debugging, intellisense, and other functions:
- XMake
- C/C++
- CodeLLDB
After completing the installation of the plugin, restart VSCode to see the status bar below:
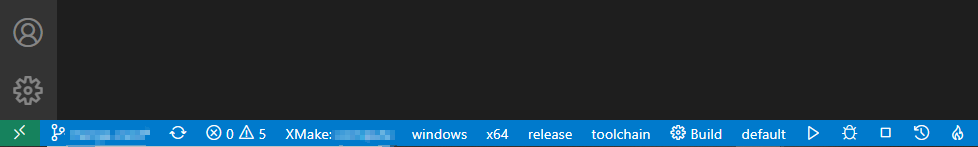
You can set the platform, architecture, compilation mode, tool-chain and other options in the status bar, and then click Build to start the build.
Debugging Support
The xmake-vscode plugin provides comprehensive breakpoint debugging support with multiple debugger types:
Debugger Types
- default: Automatically select appropriate debugger (CodeLLDB on macOS, GDB on other platforms)
- codelldb: Use CodeLLDB debugger (recommended for macOS)
- lldb-dap: Use official LLVM LLDB DAP debugger
- gdb-dap: Use GDB DAP debugger (requires C/C++ extension)
Debug Environment Requirements
Required VSCode Extensions:
- CodeLLDB: For macOS and Linux debugging (install
vadimcn.vscode-lldb) - C/C++: For GDB DAP debugging support (install
ms-vscode.cpptools) - LLDB DAP: For official LLDB debugging (install
llvm-vs-code-extensions.lldb-dap)
System Debugger Requirements:
- macOS: Need Xcode Command Line Tools (includes
lldbcommand) - Linux: Need
gdborlldbdebugger installed - Windows: Need Visual Studio Build Tools or MinGW-w64 (includes
gdb)
Installation Commands:
# macOS
xcode-select --install
# Ubuntu/Debian
sudo apt install gdb
# CentOS/RHEL
sudo yum install gdb
# Windows (using Chocolatey)
choco install gdbDebug Configuration
The xmake-vscode plugin automatically generates debug configuration and passes it to the debugger, so users don't need to manually create launch.json.
If you need to override internal debug configuration, you can use xmake.customDebugConfig setting:
{
"xmake.customDebugConfig": {
"stopAtEntry": false,
"args": ["--custom-arg"],
"env": {
"CUSTOM_ENV": "value"
}
}
}Configuration Options
The plugin supports rich configuration options that can be configured in VSCode settings:
Basic Configuration
{
"xmake.executable": "xmake",
"xmake.logLevel": "normal",
"xmake.buildLevel": "normal",
"xmake.runMode": "runOnly"
}Path Configuration
{
"xmake.buildDirectory": "${workspaceRoot}/build",
"xmake.installDirectory": "",
"xmake.packageDirectory": "",
"xmake.workingDirectory": "${workspaceRoot}",
"xmake.compileCommandsDirectory": ".vscode"
}Toolchain Configuration
{
"xmake.androidNDKDirectory": "",
"xmake.QtDirectory": "",
"xmake.WDKDirectory": ""
}IntelliSense Configuration
{
"xmake.compileCommandsBackend": "clangd",
"xmake.autoGenerateCompileCommands": "onFileChange",
"xmake.compileCommandsDirectory": ".vscode",
"xmake.enableSyntaxCheck": true
}TIP
For detailed explanation of these configuration options (such as auto-generation mode, generation path, etc.), please jump to the Configure IntelliSense section below.
Debug Configuration
{
"xmake.debugConfigType": "default",
"xmake.debuggingTargetsArguments": {
"default": ["--debug"],
"mytarget": ["--arg1", "--arg2"]
},
"xmake.runningTargetsArguments": {
"default": []
},
"xmake.envBehaviour": "merge"
}Status Bar Configuration
{
"xmake.status.showProject": false,
"xmake.status.showXMake": true,
"xmake.status.showPlatform": false,
"xmake.status.showArch": false,
"xmake.status.showMode": false,
"xmake.status.showToolchain": false,
"xmake.status.showTarget": false,
"xmake.status.showBuild": true,
"xmake.status.showRun": true,
"xmake.status.showDebug": true
}Custom options
If these options are not enough, you can create .vscode/settings.json and write the settings required by xmake, such as:
{
...
"xmake.additionalConfigArguments": [
"--my_option=true"
],
...
}Other xmake options can also be set in settings.json. After modification, the configuration can be refreshed through the >XMake: Configure command.
Configure IntelliSense
For a better C++ syntax prompt experience, xmake provides support for Language Server Protocol (LSP for short).
In VSCode, we can provide intellisense support by using vscode-cpptools or clangd.
In addition, in order to support intellisense, xmake provides compile_commands.json generation support.
generate compile_commands
Automatic trigger generation
Usually after modifying xmake.lua and clicking Save, the xmake-vscode plugin will trigger the automatic generation of compile_commands.json, which is stored in the .vscode directory by default.
This is also the recommended way. Usually after installing the xmake-vscode plugin and opening the project with xmake.lua, you only need to edit xmake.lua to save and trigger, without any other additional operations.
Manual trigger generation
Of course, if we don't see the file being generated, we can also use the >XMake: UpdateIntellisense command to manually trigger the generation of .vscode/compile_commands.json in VSCode.
Configure xmake.lua to generate automatically
Alternatively, we can also use this rule to automatically update and generate compile_commands.json
add_rules("plugin.compile_commands.autoupdate", {outputdir = ".vscode"})
target("test")
set_kind("binary")
add_files("src/*.c")This will automatically update this file after each build.
Manual execution command generation
If the above methods are invalid, we can also execute the command to generate it.
$ xmake project -k compile_commands .vscodeIntelliSense Configuration
{
"xmake.compileCommandsBackend": "clangd",
"xmake.autoGenerateCompileCommands": "onFileChange",
"xmake.compileCommandsDirectory": ".vscode",
"xmake.enableSyntaxCheck": true
}If we use the vscode-cpptools plugin to provide intellisense support, we need to go to the VSCode plugin marketplace first, search for C++, and install the default first plugin.
When installed, this plugin provides intellisense and debugging support.
Then, we need to configure the c_cpp_properties.json file and associate it with the .vscode/compile_commands.json we generated.
{
"env": {
"myDefaultIncludePath": ["${workspaceFolder}", "${workspaceFolder}/include"],
"myCompilerPath": "/usr/local/bin/gcc-7"
},
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Mac",
"intelliSenseMode": "clang-x64",
"includePath": ["${myDefaultIncludePath}", "/another/path"],
"macFrameworkPath": ["/System/Library/Frameworks"],
"defines": ["FOO", "BAR=100"],
"forcedInclude": ["${workspaceFolder}/include/config.h"],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"compileCommands": "/path/to/compile_commands.json",
"browse": {
"path": ["${workspaceFolder}"],
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": ""
}
}
],
"version": 4
}That is the "compileCommands": "/path/to/compile_commands.json" configuration item above.
For how to open this configuration file, and more configuration instructions, see:
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/configure-intellisense-crosscompilation
- https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/cpp/c-cpp-properties-schema-reference
Of course, in theory, the xmake-vscode plugin can automatically associate and set this file, but considering that users do not necessarily use cpptools, they may also use clangd.
Therefore, the default automatic configuration is not very good, and the author has no time and energy to improve it.
clangd
When using clangd, there may be conflicts with the C/C++ plugin, you can add settings in .vscode/settings.json:
{
"C_Cpp.codeAnalysis.runAutomatically": false,
"C_Cpp.intelliSenseEngine": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.formatting": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.autoAddFileAssociations": false,
"C_Cpp.autocompleteAddParentheses": false,
"C_Cpp.autocomplete": "Disabled",
"C_Cpp.errorSquiggles": "Disabled",
...
}Also, since the compile_commands.json generated by XMake is in the .vscode directory, you need to set the clangd parameter to look for it in the correct location:
{
"clangd.arguments": [
"--compile-commands-dir=.vscode",
...
]
...
}Intellij IDEA/CLion Plugin
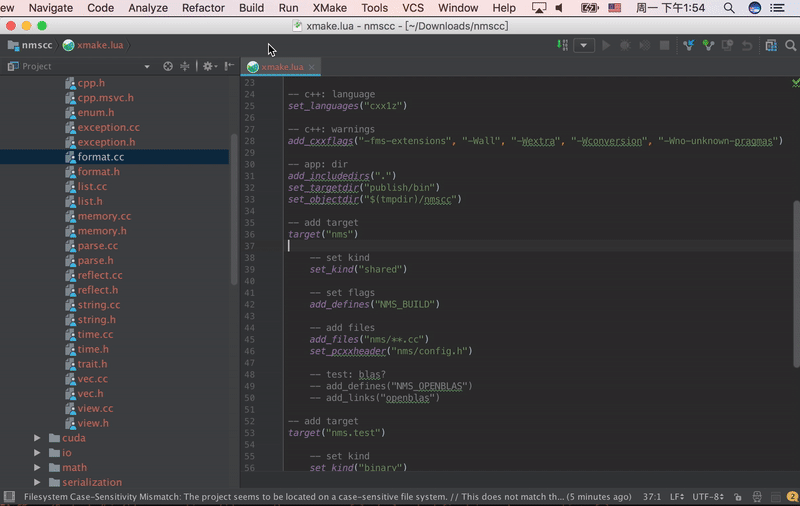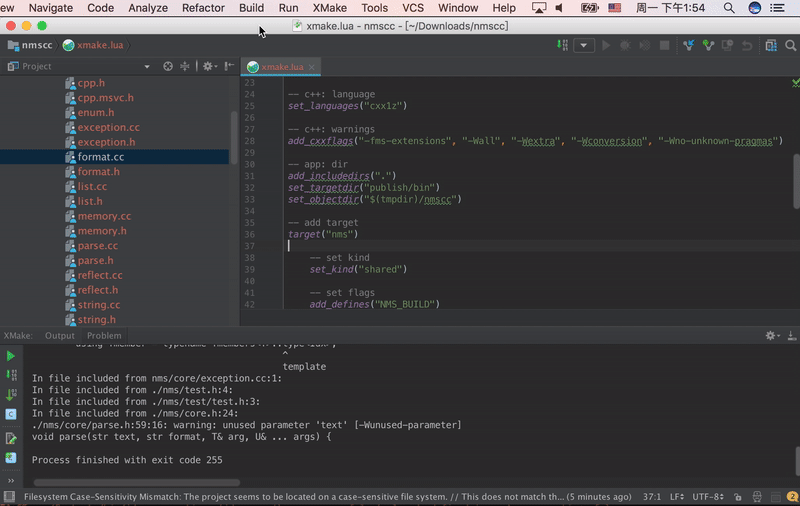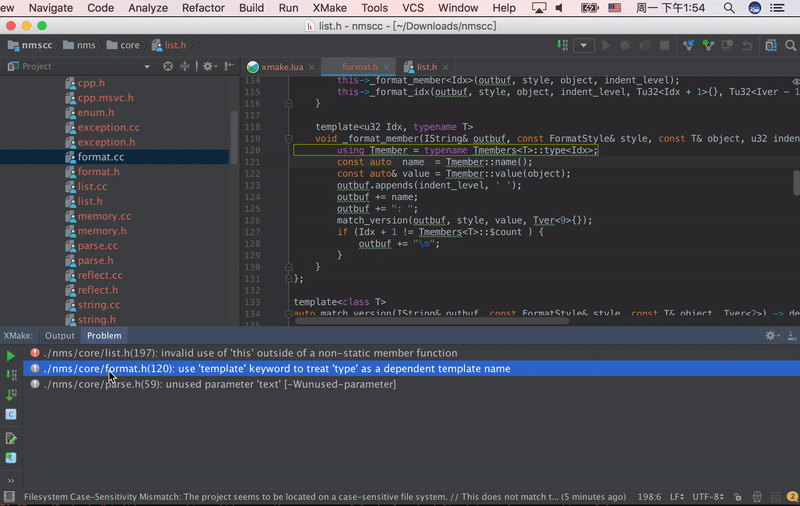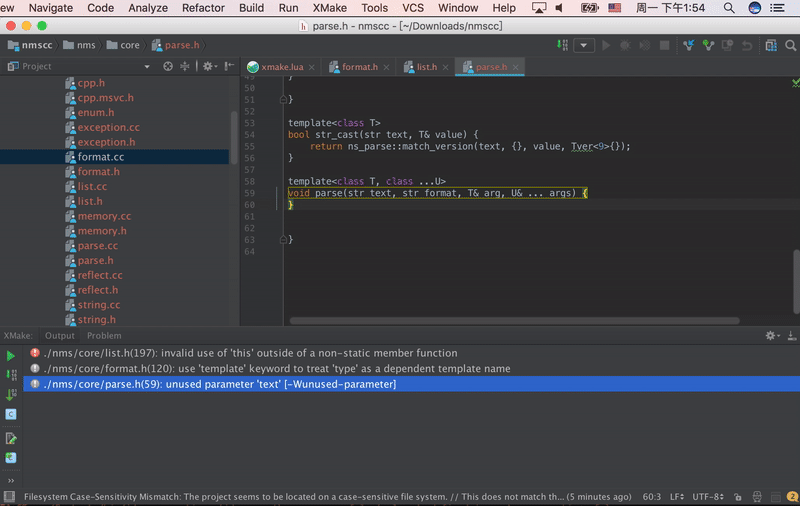
CLion 2025.3+ New Feature: Supports lldb/gdb-dap debugging, allowing you to debug Xmake projects directly without needing to generate CMakeLists.txt as a workaround. You can set breakpoints, step through code, and view variable values.
Debug configuration interface:
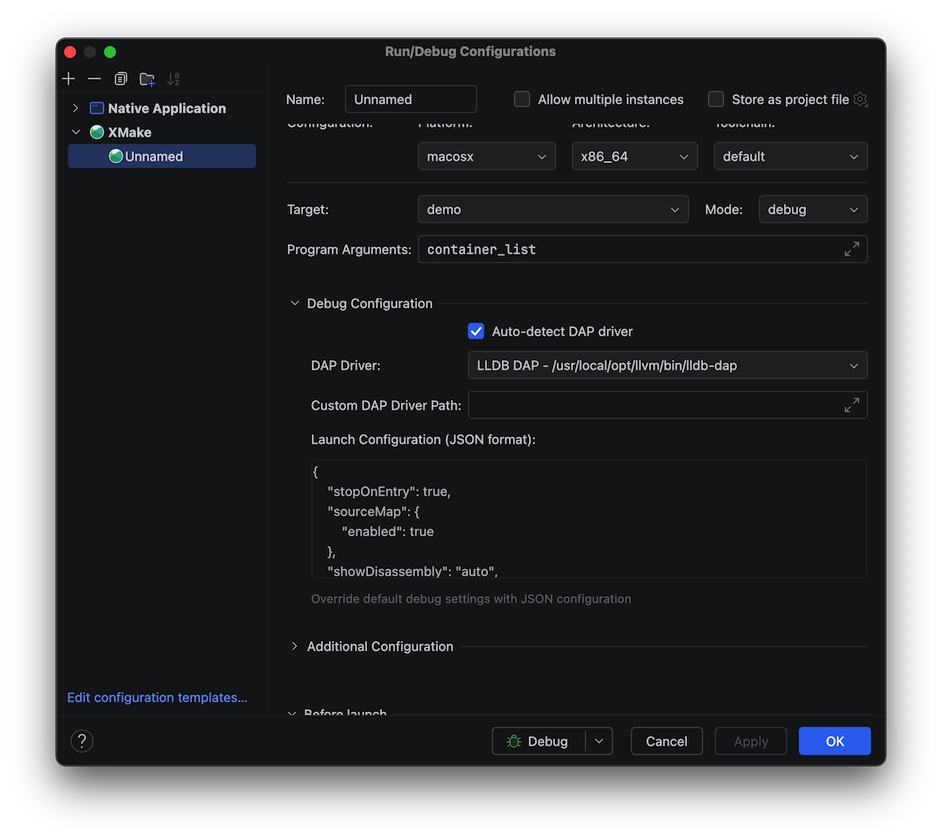
Runtime debugging interface:
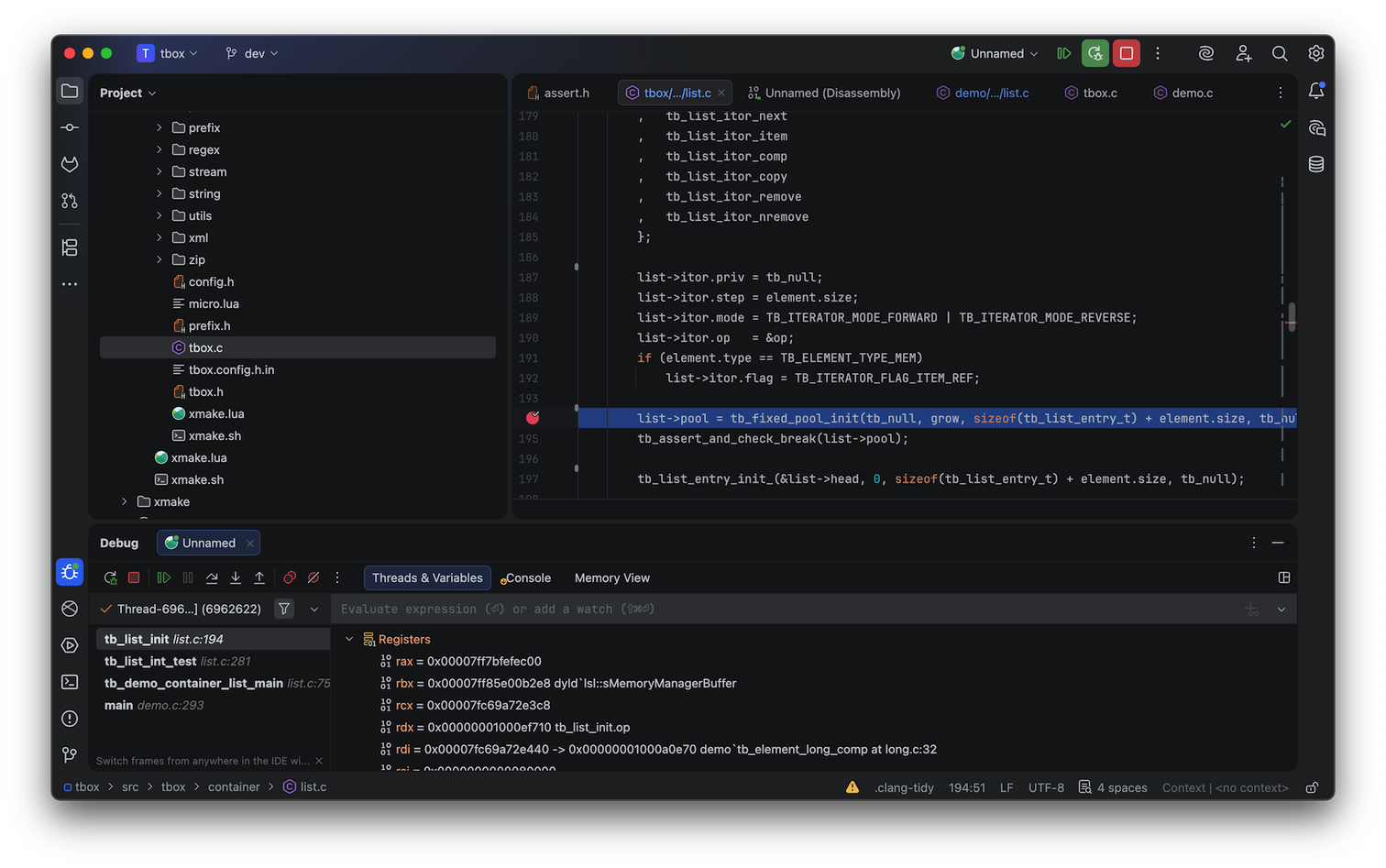
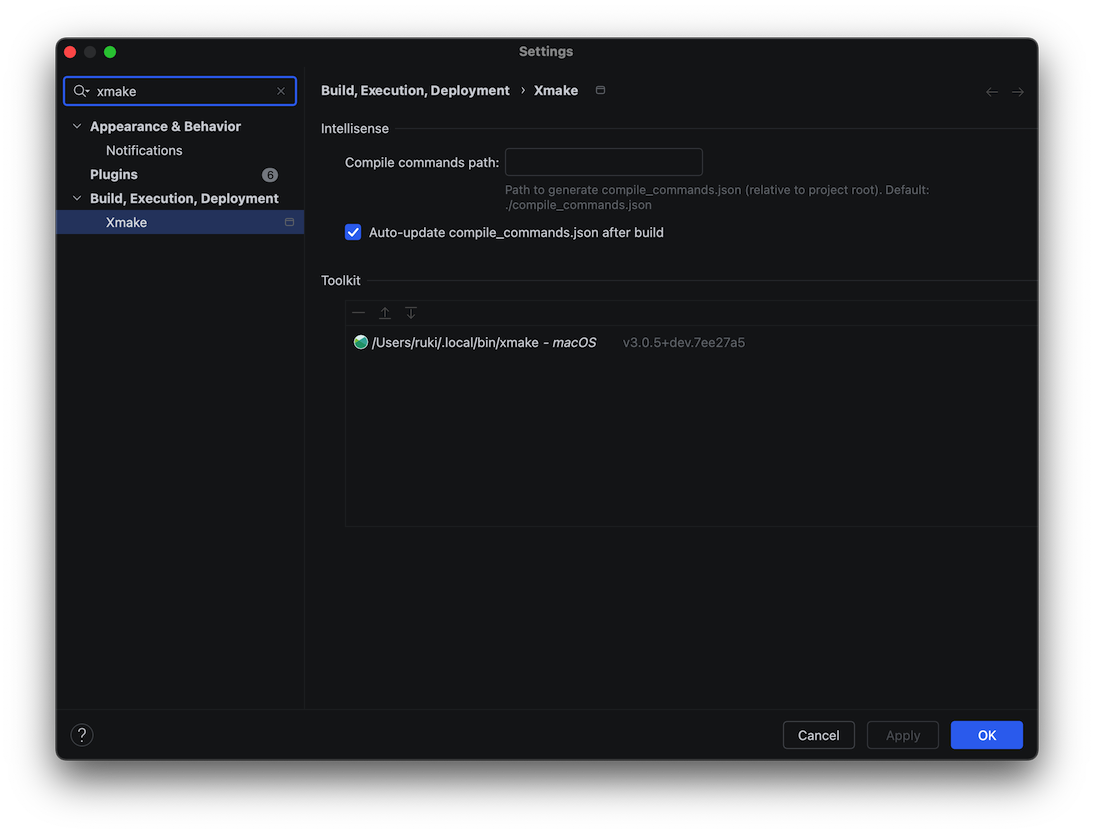
Additionally, the plugin now supports automatic updating of compile_commands.json to improve C++ code completion and highlighting experience.
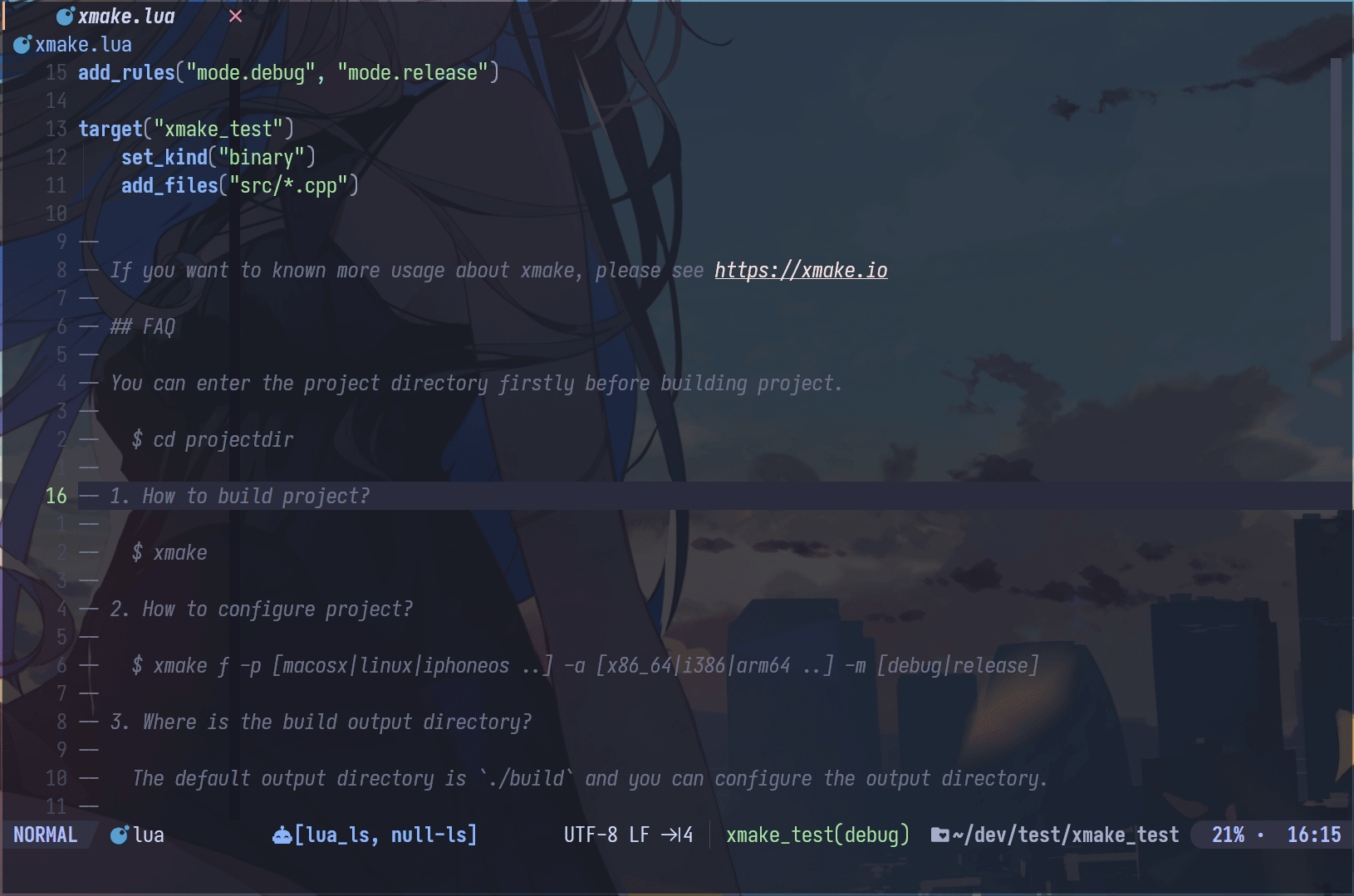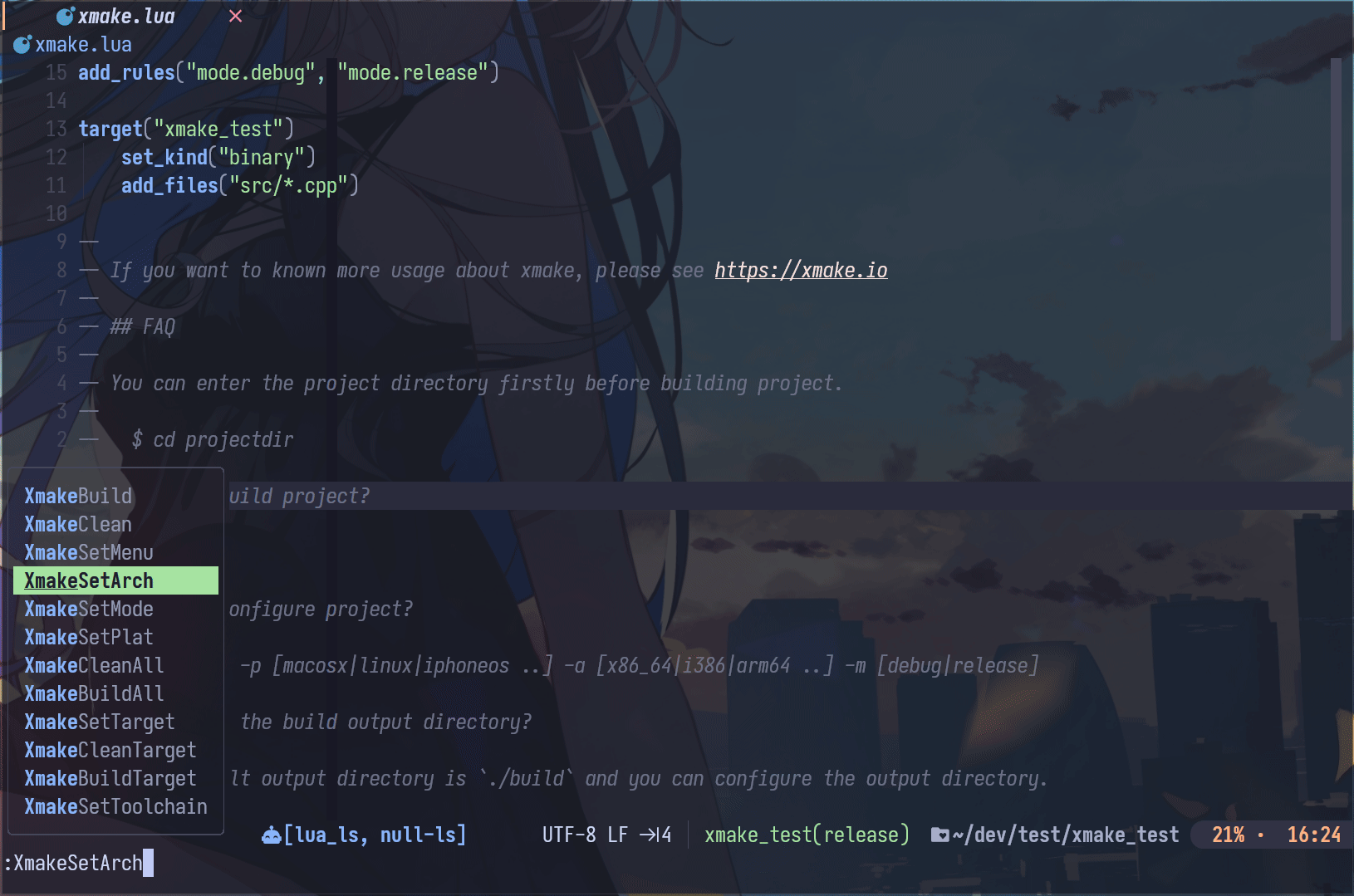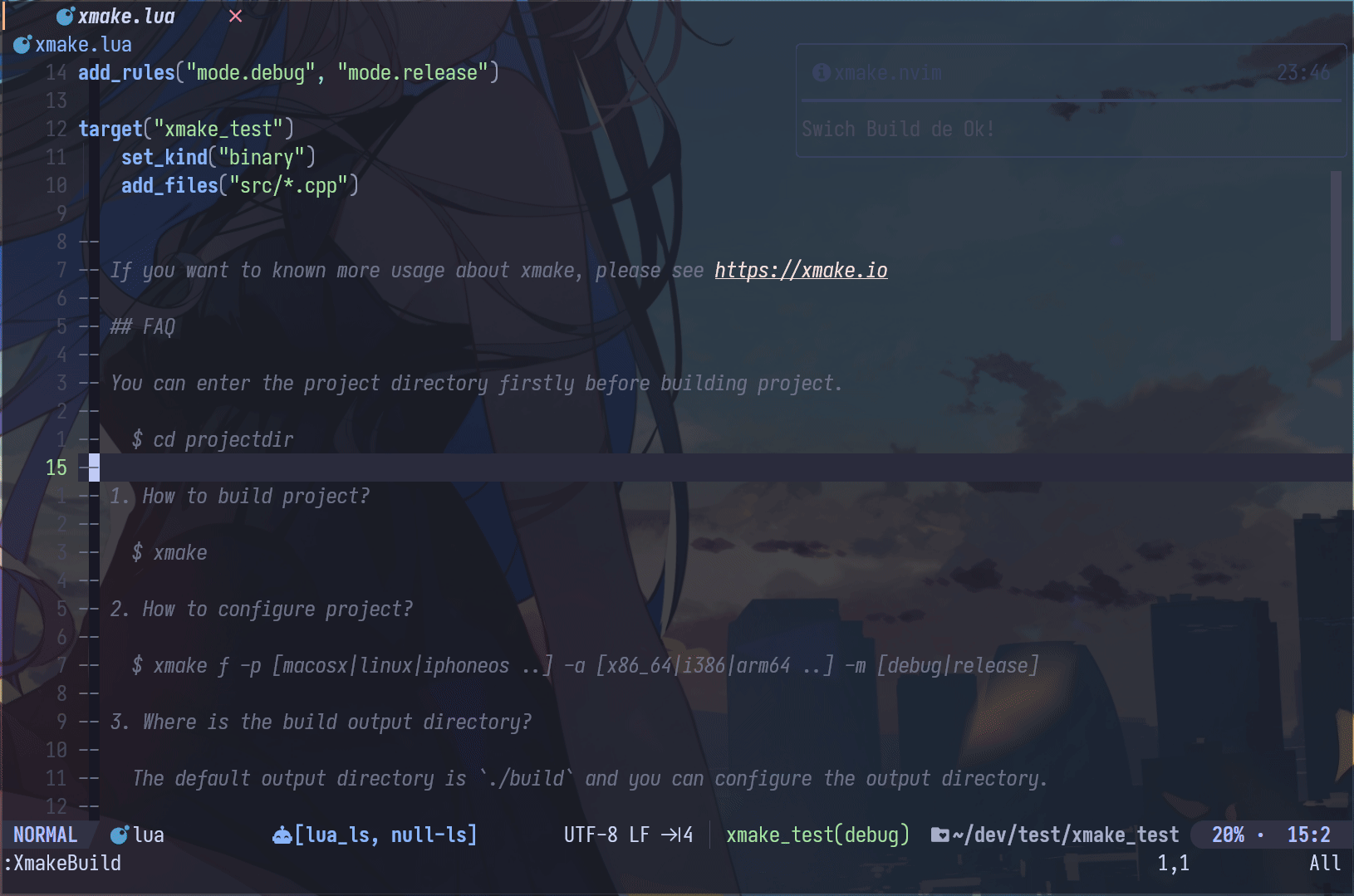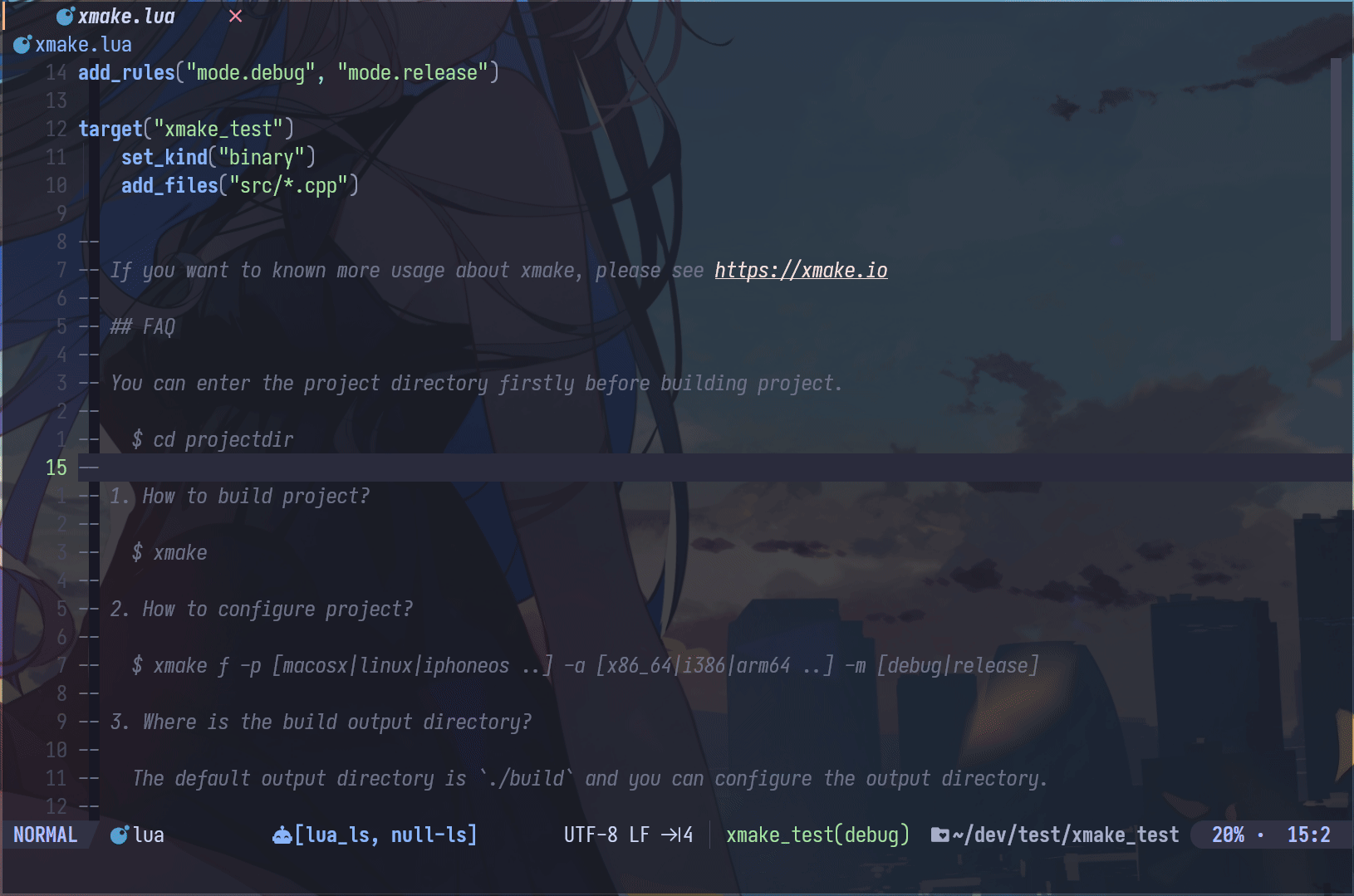
Neovim Plugin
- xmake.nvim (third-party, thanks @Mythos_404)
The plugin provides an easy-to-use configuration UI and auto-generation of compile_commands.json files
Zed Editor Plugin
Zed is a high-performance, multiplayer code editor, and xmake provides plugin support for it.
Plugin installation
The Zed editor plugin provides seamless integration with xmake, offering features like:
- Project configuration and build management
- Real-time build status and error reporting
- IntelliSense support through compile_commands.json generation
- Quick access to common xmake commands
::: note The plugin is currently being submitted to the official Zed marketplace and is pending review (PR #4565). In the meantime, you can install it locally: :::
Local Installation
Clone the plugin repository:
shgit clone https://github.com/xmake-io/xmake-zed.gitLoad the extension in Zed:
- Open Zed editor
- Go to
Zed > Extensions - Click
Load Extensionand select the clonedxmake-zeddirectory
Marketplace Installation (Future Support)
Once the official review is approved, you'll be able to install it directly from the Zed marketplace by going to Zed > Extensions, then search for xmake and install the official plugin.
Usage
After installation, the plugin will automatically detect xmake projects and provide:
- Full LSP Support: Code completion, diagnostics, hover info, code actions, symbol navigation, and formatting via xmake_ls
- Syntax Highlighting: Support for 300+ XMake API functions
- Project Templates: 25+ project templates covering 15 programming languages
- Auto-installation: Automatically downloads and installs xmake_ls language server
TIP
The plugin will automatically download and install the xmake_ls language server, no manual configuration required.
Configuration
The plugin supports the following main configuration options:
{
"lsp": {
"xmake-ls": {
"settings": {
"linuxVariant": "auto",
"logLevel": "Info",
"enableDiagnostics": true,
"enableCompletion": true,
"enableHover": true,
"enableCodeActions": true,
"xmakePath": ""
}
}
}
}Key options:
- linuxVariant: Linux binary variant (auto/musl/x64 etc.)
- logLevel: Log level (Error/Warning/Info/Debug/Trace)
- enableDiagnostics/Completion/Hover/CodeActions: Enable/disable features
- xmakePath: Path to xmake executable
Gradle Plugin (JNI)
- xmake-gradle: A gradle plugin that integrates xmake seamlessly
plugins DSL
plugins {
id 'org.tboox.gradle-xmake-plugin' version '1.2.3'
}Legacy plugin application
buildscript {
repositories {
maven {
url "https://plugins.gradle.org/m2/"
}
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.tboox:gradle-xmake-plugin:1.2.3'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
}
apply plugin: "org.tboox.gradle-xmake-plugin"Simplest Example
We add xmake.lua to projectdir/jni/xmake.lua and enable xmake in build.gradle.
build.gradle
android {
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
path "jni/xmake.lua"
}
}
}JNI
The JNI project structure:
projectdir
- src
- main
- java
- jni
- xmake.lua
- *.cppxmake.lua:
add_rules("mode.debug", "mode.release")
target("nativelib")
set_kind("shared")
add_files("nativelib.cc")More Gradle Configuations
android {
defaultConfig {
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
// append the global cflags (optional)
cFlags "-DTEST"
// append the global cppflags (optional)
cppFlags "-DTEST", "-DTEST2"
// switch the build mode to `debug` for `xmake f -m debug` (optional)
buildMode "debug"
// set abi filters (optional), e.g. armeabi, armeabi-v7a, arm64-v8a, x86, x86_64
// we can also get abiFilters from defaultConfig.ndk.abiFilters
abiFilters "armeabi-v7a", "arm64-v8a"
}
}
}
externalNativeBuild {
xmake {
// enable xmake and set xmake.lua project file path
path "jni/xmake.lua"
// enable verbose output (optional), e.g. verbose, warning, normal
logLevel "verbose"
// set c++stl (optional), e.g. c++_static/c++_shared, gnustl_static/gnustl_shared, stlport_static/stlport_shared
stl "c++_shared"
// set the given xmake program path (optional)
// program /usr/local/bin/xmake
// disable stdc++ library (optional)
// stdcxx false
// set the given ndk directory path (optional)
// ndk "/Users/ruki/files/android-ndk-r20b/"
// set sdk version of ndk (optional)
// sdkver 21
}
}
}Build JNI and generate apk
The xmakeBuild will be injected to assemble task automatically if the gradle-xmake-plugin has been applied.
$ ./gradlew app:assembleDebug
> Task :nativelib:xmakeConfigureForArm64
> Task :nativelib:xmakeBuildForArm64
>> xmake build
[ 50%]: cache compiling.debug nativelib.cc
[ 75%]: linking.debug libnativelib.so
[100%]: build ok!
>> install artifacts to /Users/ruki/projects/personal/xmake-gradle/nativelib/libs/arm64-v8a
> Task :nativelib:xmakeConfigureForArmv7
> Task :nativelib:xmakeBuildForArmv7
>> xmake build
[ 50%]: cache compiling.debug nativelib.cc
[ 75%]: linking.debug libnativelib.so
[100%]: build ok!
>> install artifacts to /Users/ruki/projects/personal/xmake-gradle/nativelib/libs/armeabi-v7a
> Task :nativelib:preBuild
> Task :nativelib:assemble
> Task :app:assembleDebugForce to rebuild JNI
$ ./gradlew nativelib:xmakeRebuildSublime Plugin